The deadly truth about Giadia
This dreadful, potentially deadly parasite is a very resilient and spreads easily. As little as ten parasites can easily multiply and spread over many hundreds of kilometers in weeks, if not days.
Giardia Lamblia, also known as Giardia intestinalis, Giardia lamblia, or Giardia duodenalis, is devastating for not only humans but also animals. This parasite lives in the intestines of humans/animals. The parasite would cause a severe, if not deadly, an illness called Giardiasis.
As the Giardia parasite lives in the intestines, the parasite is present in the faces of an infected person/animal.

So what is actually Giardia Lamblia?
It is a flagellated protozoan parasite, single cell. This microorganism is unicellular eukaryotes (defined as Protozoans). It is part of the Eukaryote Domain, Metamonada of Phylum, Diplomonadida of the order, it is part of the Hexamitidae family, and the Genus is the Giardia, the species is referred to as G. lamblia, and the Binomial name is Giardia lamblia.
When the cysts become a trophozoite in its life cycle, it tends to accumulate. They are grouped in a formation (karyosome) that resembles a nucleolus though it lacks any complex DNA or RNA (chromatin). This unicellular microorganism lacks a membrane enclosure (mitochondrion). The cyst is able to live within itself (endosymbiont).
The cyst has four nuclei and withdrawn cytoplasm. As you can see by the picture, under a magnification, Giardia Lamblia has an appearance of a clown’s face or appearance of a halo on the two nuclei.
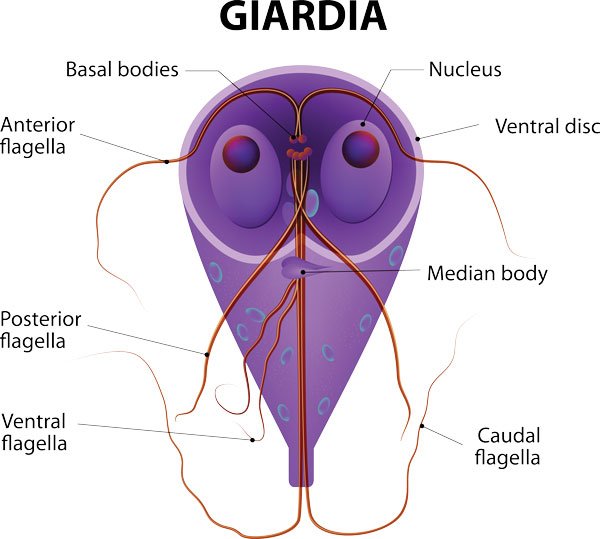
Are the Giardia cysts/parasites hardy?
The Giardia cysts are extremely hardy;
- Surviving extreme temperatures,
- Moisture,
- Dryness
- Low level of UV
- Surviving attacks from other organisms.
- Surviving water chemical purification
How big are these parasites?
The Giardia lamblia parasite size ranges from 2 to 8 microns in size.
What is the lifespan of these parasites?
These parasites can live upto 7 weeks in a cool environment and less in a warmer environment.
What is the difference between a cyst and a parasite?
There is really no difference. A cyst is a stage of some versions parasites during when are covered in a protective wall
How do you catch it?
The primary way to catch this parasite is when the parasite enters a person through the mouth, though it can be caught through oral or anal sex. The manner to catch Giardiasis is via direct or indirect contact with feces into a person’s digestive system. This can happen many ways, for example;
- From a door handle in a bathroom where the person previously in the bathroom has Giardiasis touch the door handle
- Animal droppings in the drinking water reservoir
- If camping and using the tarpaulin to capture the water, the slightest animal dropping on the tarpaulin can infect the water
- People who have Giardiasis, and swim in the swimming pool. It can spread like wildfire, or
- Being in contact with someone with Giardiasis• Eating food that has been washed with infected Giardia
- From ingesting water that is contaminated with the parasite, whether town supply, bottled water, drinking directly from a stream/water supply.
There are numerous other ways to catch this nasty parasite,
What is Giardia Lamblia’s lifecycle?
The lifecycle of this parasite is relatively uncomplicated, considering the damage it can have on human life. The cycle begins;
Phase 1; Digestion of Giardia cysts. (The infectious stage of the parasite)
Phase 2; In the small intestines (duodenum), where ph levels of the stomach are low, produces encystations that break the cysts shell releasing trophozoite.
Phase 3; Once in the small intestine, the trophozoite starts reproducing through an asexual process (longitudinal binary fission). They can either attach themselves to the wall of the intestine(mucosa of the lumen) or just ‘hang around”.
Phase 4; Some of the cysts and trophozoite are then passed through the bodies system in the form of feces (stools)Phase 5; Once out of the body, the cysts are then able to spread in several ways but not necessarily multiple
Next is another diagram of the process showing it more detail.
Does the Giardia have and borders or limits?
Giardia has no borders. It is a genuinely international parasite residing in all countries around the world.
Is Giardiasis contagious?
Giardiasis is extremely contagious. It spreads like wildfire. Fanatical care needs to taken to avoid spreading or catching the “parasite.” For example, do not swim in pools, avoid public toilets and showers, avoid town water, and be wary of bottled water (you may just be paying for the bacteria) you get the picture.
How many parasites do you need to catch Giardiasis?
Only one parasite! It can hide itself in many thousands of litres of water. That makes it extremely hard to detect and is not eliminated with chemicals such as iodine and chlorine.
What are the symptoms of Giardiasis?
When there is an establishment of Giardia Lamblia, this results in the infection called Giardiasis. The symptoms are some/combination of;
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Gut Bloating
- Malaise
- Stomach cramps
- Vomiting
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Reduces food absorption
- Diminished Appetite
- Excessive Gas – the gas is often very strong disgusting odor that can make you nauseous
- Dehydration
- Greasy stools that tend to float
- Feces covered in mucus and/or blood
- Explosive diarrhea
Do all people show symptoms of Giardia?
Some people may not exhibit symptoms of Giardia though they may be unknowingly being carriers of this vicious parasite.
Can you die from Giardiasis?
In extreme cases, and for the young, elderly, or the unwell, these parasites can cause death. The common cause of death is dehydration, as there is a rapid loss of fluids during the illness/infection.
How long before I start noticing Giardiasis symptoms?
On average, the incubation period is 7 days from being exposed to the parasite though it is known that it may be as long as 14-21 days.
How long will Giardiasis last?
Here is the sad news for a healthy person anywhere from 14 to 100’s days. There are known cases where it lasts for several months. Always see a doctor for medical advice for recovery.
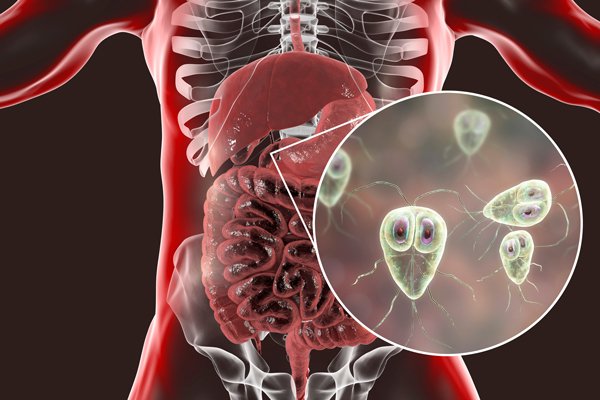
What are the impacts of catching Giardia?
Giardiasis is a severe body infection that may cause death to people. Children are almost three times the risk of catching it than adults.
Some of the potential impacts of getting over this infection are;
- Weight loss
- Severe dehydration
- About 40% of people are disaccharide intolerant for up to six months.
- Become intolerance to lactose. This includes milk, yogurt for up to several months
- Severe cases can lead to malabsorption syndrome
- Reduction of life expectancy for those with immune deficiency
Who can catch Giardiasis?
Giardia lamblia is indiscriminate. Everyone can catch it. The people who most at risk of catching Giardiasis are the young, the elderly, the frail, those who have weak immune systems, those living in large share living areas, people are working at daycare centers, hikers, and those traveling.
How do you know or your doctors know if you have Giardiasis?
It is very difficult to diagnosis externally. The best way to diagnose is by testing your feces using an antigen test. Quite often, multiple feces need to be tested as they may necessarily come out each time.
Can you catch it from blood?
No, a parasite is not present in the blood.
Is there a treatment for Giardiasis?
The most common treatment is metronidazole. Other treatments are tinidazole or nitazoxanide, i.e., prescription medications. This works about 85% of the time but causes some side effects, including nausea as well as dizziness and headaches. Extreme care should be taking of metronidazole as it is carcinogenic.
Like always, always contact your doctor before taking any medicine. Despite the effectiveness, it is not approved by the FDA in the US for the treatment of Giardiasis.
Another popular treatment is berberine sulfate found naturally in plants. High dosages of berberine can lead to unwanted side effects such as hypotension. Always seek medical advice when looking for treatment.
Is Giardiasis preventable?
Where do you start! Technically yes, but it is extremely hard. You can reduce the risk of catching it by just having good hygiene practice, avoid drinking directly from rivers, streams, and the like. Avoid swimming in a very crowded swimming pool.
If in doubt, here are some other ways to avoid Giardia;
- Eat only peeled fruit and vegetables
- Only eat cooked food
- Drink filtered or boiled water (minimum of 1 minute) only. Note the water filter must remove all parasites and bacteria larger than 1 micron to be effective
- Only drink bottled water from well-known brands and in reliable countries
Can Giardiasis survive frozen water, ice?
These parasites are very, very tuff. They can survive frozen water, ice. You can catch Giardiasis from ice!
Can Giardia Parasite live outside feces?
Giardia is extremely hardy. Only the cysts are able to live outside the feces during its lifecycle. During the trophozoite phase, it survives in feces, though it will perish very soon as it has insufficiently developed.
Is it easy to detect?
Giardia lamblia is very hard to detect. Giardia lamblia being of only 2-5 microns makes it hard to detect using standard measurement techniques.
For personal testing, the doctor will take a sample of your stool and ask the laboratory to test for the cyst. Several stools may be required. The tests may take several days.
In water, the concentration of these parasites may be very sparse, so when testing water samples, several thousand litres are needed to be tested to assess. This makes it extremely hard for water treatment to assess whether or not they pass this on to consumers.
Can Chlorine or Iodine destroy Giardia?
Giardia cysts are resistant to conventional water treated methods such as chlorination and ozonolysis. The levels of concentrate required to destroy the cysts are very high as it requires penetrating the hard shell of the parasite. By using high levels of chemicals, it makes the water undrinkable.
The US Army has found the low dosage of iodine and chlorine is in-effective against this hard sell cyst.
The best method avoiding this parasite is by the physical removal by using a filtration system, like the Survival Jerrycan.
Can municipal water treatment plants remove Giardia?
Not all municipal water treatment plants can filter out the Giardia from our water sources. As technology improves and investments being made, water treatment plants are improved to remove this infectious parasite.
UV treatment has been found to be an excellent technology to destroy the Giardia cyst.
Really, how serious should be taken Giardia?
Absolutely, some statistics are extremely frightening. They include;
- Over 80 million people, globally, suffer from Giardia every single year.
- Over 2 million people die from Giardia related illnesses.
- Some 46% of water tested in drinking water sources across America tested positive to traces of Giardia
- Some 40% of people who traveled to an overseas country contracted some type of gastroenteritis that made them uncomfortable for a least 1 day, and some 4% of people are ill for more the 3 days plus
- Giardia Lamblia is implicated in 25% of gastroenteritis cases.
- It is estimated that this parasite infects over 2% of people.
- This infection is prevalent in homosexual men spread through sexual transmission.




